The Department of Homeland Security has increased fines for Form I-9 paperwork violations and the hiring of unauthorized workers.
Under fine adjustments published in the Federal Register on January 13, the new penalty amounts for paperwork violations are:
• Minimum fine: $272
• Maximum fine: $2,701.
Violations for knowingly hiring, recruiting, referring, or retaining unauthorized aliens (per unauthorized alien) are:
• $676 to $5,404 for a first offense
• $5,404 to $13,508 for a second offense
• $8,106 to $27,108 for a third offense.
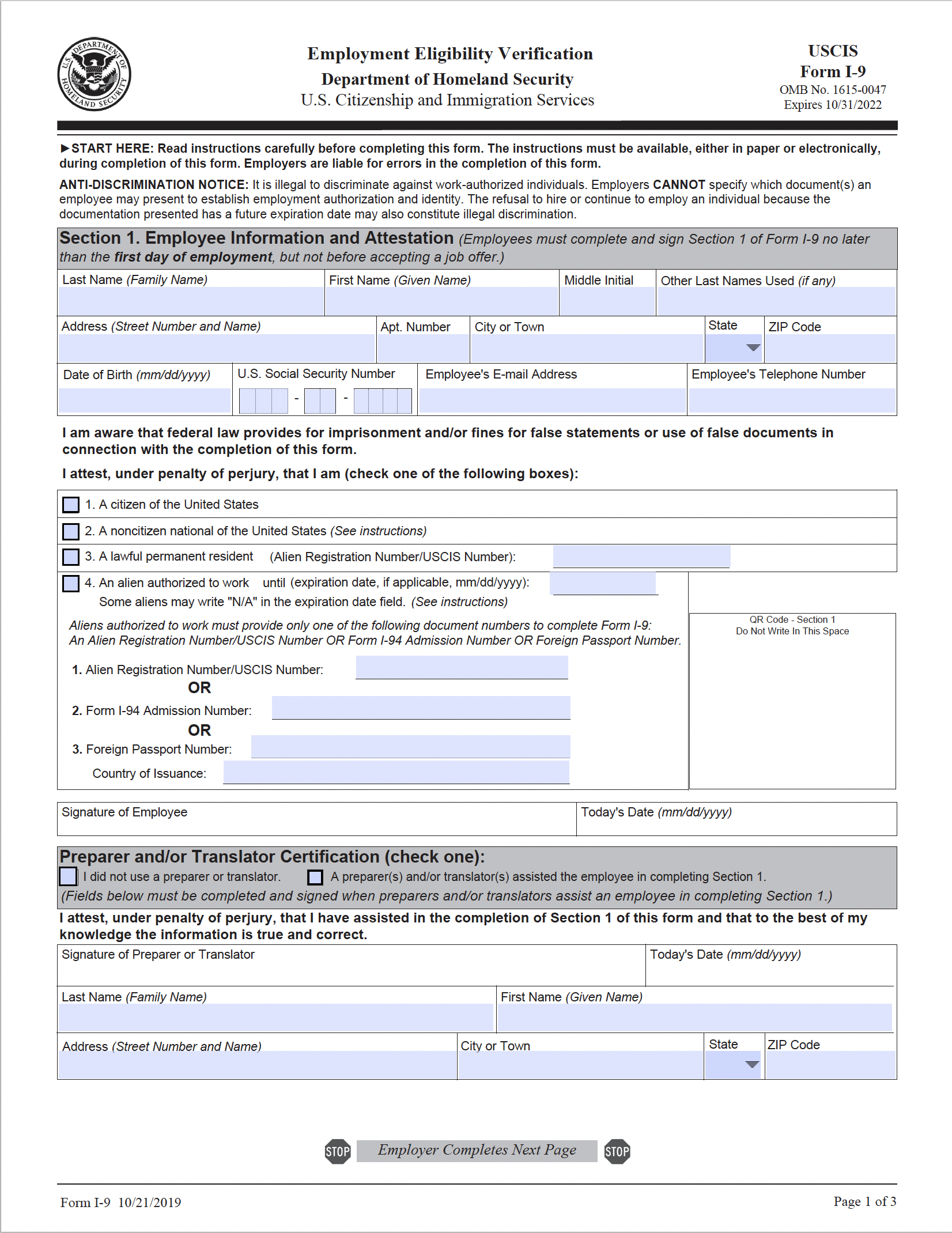
When do employers use the Form I-9?
The Form I-9 is completed when an employee begins work. Employers use the form to verify the identity and employment authorization of each worker who is hired.
Section 1 of the form must be completed by a new employee on or before the first day of work, and the employer completes Section 2 of the form within three business days after the employee starts work. Section 3 is completed when required.
What factors are taken into account when Form I-9 penalties are assessed?
The U.S. Immigration and Customs Service (ICE) assesses violations relating to the Form I-9. When determining the amount of the penalty, it considers:
• The size of the employer’s business
• The good faith of the employer
• The seriousness of the violation
• Whether or not the individual was an unauthorized alien
• A history of previous violations.
How can employers avoid
Form I-9 penalties?
Employers should train staff members to correctly complete the Form I-9. The form is detailed and contains a number of potential stumbling blocks relating to:
• Employee information
• Signatures
• Dates
• Documents presented for review.
An employer should regularly conduct Form I-9 audits to ensure that the form has been properly completed for all employees.
If mistakes are found, the errors can be corrected. However, employers should also update their procedures and train employees so the same errors are not made again.
Copyright J.J. Keller & Associates, Inc. Printed with permission.